Architecture
ZKPDF enables zero-knowledge verification of PDF documents through cryptographic proofs. The system consists of three main components: PDF processing utilities, zero-knowledge circuits, and a web application.
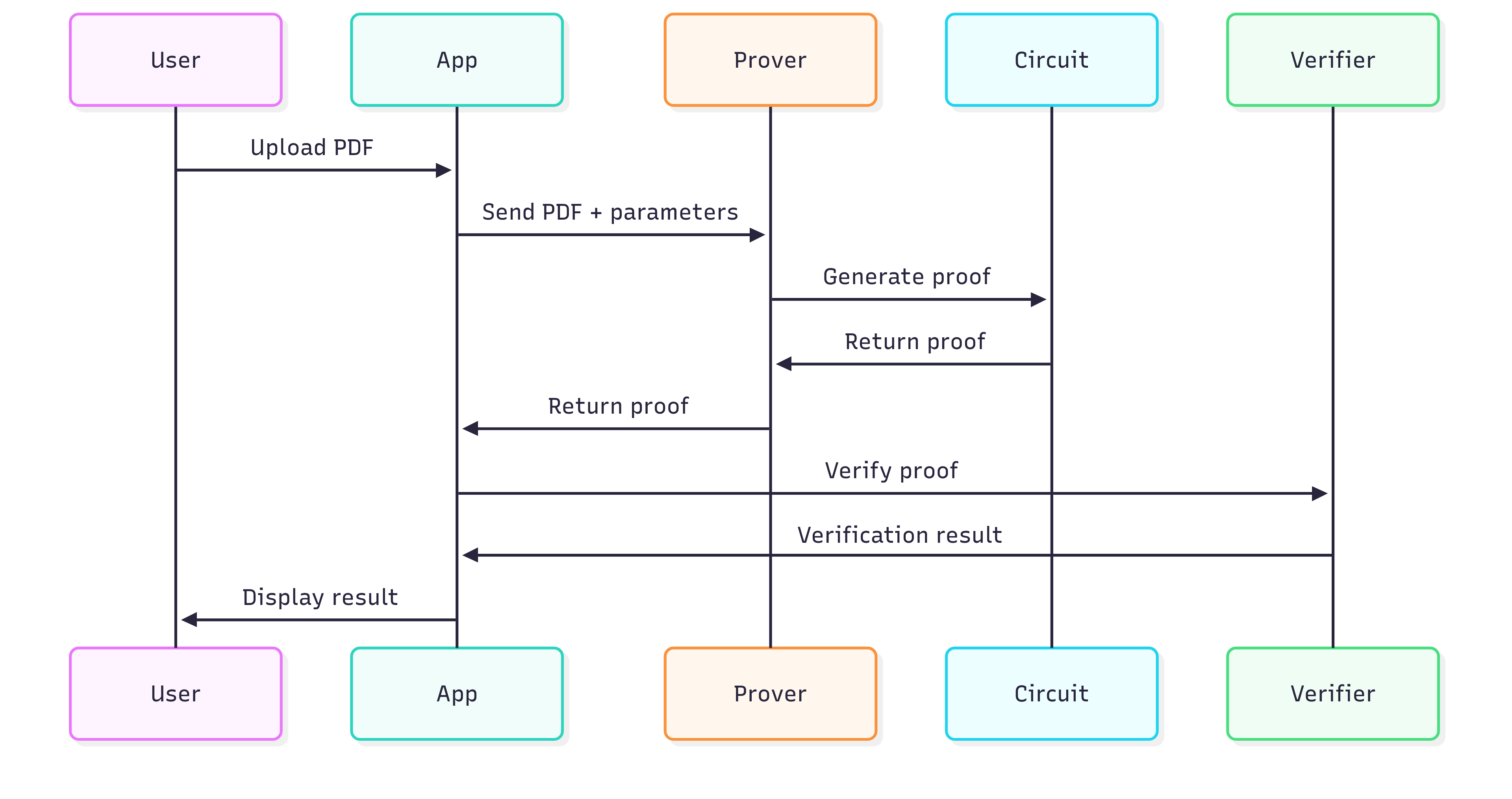
System Overview
The verification process:
- PDF document is parsed to extract text and validate digital signatures
- Verification claims are processed through SP1 zero-knowledge circuits
- Cryptographic proofs are generated without revealing document content
- Proofs can be verified on-chain or off-chain
Core Components
PDF Utils (pdf-utils/)
Rust-based PDF processing library designed for zero-knowledge environments. Provides text extraction, signature validation, and unified verification interface with WebAssembly support for browser compatibility.
Circuits (circuits/)
SP1-compatible zero-knowledge circuits containing the main verification library, SP1 program implementation, and proving infrastructure utilities.
App (app/)
Next.js frontend application providing PDF upload, real-time verification, proof generation, and integration with the prover server and WASM modules.
Data Flow
PDF Processing
- Document upload through web interface
- Client-side parsing using WebAssembly
- Text and signature extraction
- Initial validation
Proof Generation
- PDF data prepared for SP1 circuits
- SP1 zkVM executes verification program
- Zero-knowledge proof generated
- Public values committed to proof
Verification
- Proof validated locally or on-chain
- Results displayed without revealing document content
PDF Support
| Feature | Support |
|---|---|
| Text extraction | ✅ |
| RSA-SHA256 signatures | ✅ |
| Multi-page documents | ✅ |
| Common font encodings and CID fonts | ✅ |
| Standard PDF structures and compression | ✅ |
| Image extraction | ❌ |
| Form fields | ❌ |
| ECDSA signatures | ❌ |
| Complex layouts and advanced font features | ❌ |
Performance Characteristics
- Large PDFs require significant memory (8-16GB)
- Proof generation: 20-3 mins depending on mode
- Browser memory limitations for file processing